Safely cooling foods is an essential practice in both the food service industry and home cooking. It helps maintain food quality and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. There are various methods of cooling foods, but choosing the most effective and practical one can make a significant difference in food safety.
One of the well-known methods for cooling food is using a blast chiller, which rapidly decreases the temperature of cooked food to minimize the time spent in the temperature danger zone. However, not everyone has access to this specialized equipment, so it’s important to consider alternative options for safely cooling foods.
A highly recommended alternative to blast chillers is the ice bath technique. This method involves immersing a container of hot food into a mixture of ice and water, which promotes efficient cooling while maintaining food safety standards. By employing this convenient and accessible technique, individuals can ensure they’re safely cooling foods to protect the health of consumers and maintain the taste and quality of their dishes.
Reader's Roadmap
Understanding the Basics
When it comes to food safety, properly cooling foods is an essential practice. Safely cooling foods helps prevent the growth of microorganisms, such as bacteria, which can lead to foodborne illnesses. The temperature danger zone of 41°F to 135°F (5°C to 57°C) is where bacteria can multiply rapidly, thus it is crucial to bring the temperature of food out of this range as quickly as possible.
Temperature control is particularly important for time and temperature control for safety (TCS) foods. TCS foods are those that require specific time and temperature measures to prevent the growth of harmful pathogens. Examples of TCS foods include meat, dairy products, cut fruits and vegetables, and cooked grains, among others. Ensuring proper cooling methods for these types of foods is a crucial step for maintaining food safety.
One of the most effective ways to safely cool foods is by using an ice bath. After hot foods have been cooked or reheated to appropriate temperatures, they should be divided into smaller, shallow containers that are no more than 4 inches deep. Placing these containers into an ice water bath helps to rapidly decrease the temperature of the food, minimizing the time spent in the temperature danger zone.
In addition to using ice baths, it is also important to consider the type of container used to store the food. Insulated containers may slow down the cooling process, while containers made from materials that allow for quicker heat transfer, such as stainless steel or aluminum, can facilitate more rapid cooling.
By understanding and employing the best alternatives for safely cooling foods, you can greatly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensure the well-being of those consuming the food. With the right approach and attention to detail, food safety can be maintained while still delivering delicious and enjoyable meals.
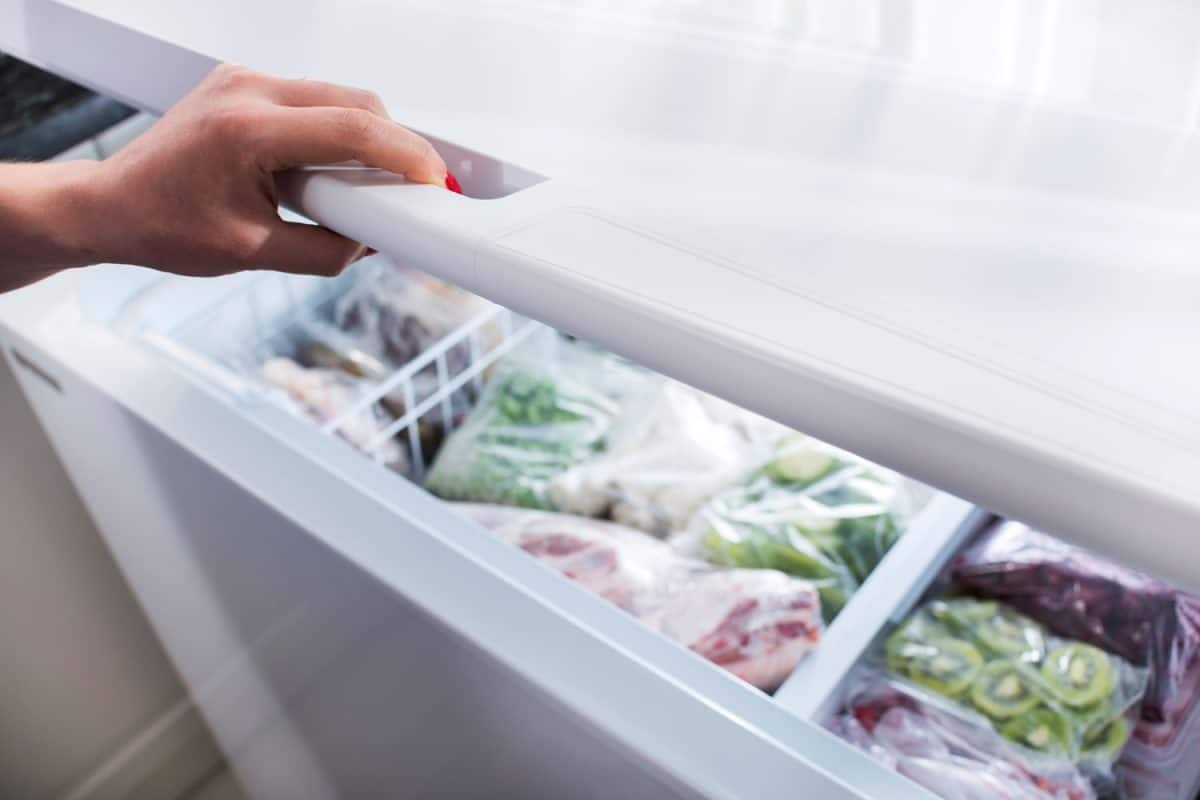
Refrigerator and Freezer
Role in Cooling Foods
Refrigerators and freezers play an essential role in safely cooling and storing food. They maintain optimal temperatures for preserving perishable items, maintaining freshness and inhibiting bacteria growth. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advises keeping refrigerator temperatures at or below 40°F (4°C) and freezer temperatures at or below 0°F (-18°C). However, a refrigerator temperature range of 35° to 38°F (1.7 to 3.3°C) is ideal to keep foods as close to freezing as possible without actual freezing.
In addition to temperature settings, proper organization inside refrigerators and freezers also plays a significant part in food safety. Storing raw meats on the bottom shelves helps to prevent cross-contamination from dripping juices contaminating other foods. Moreover, placing cooked and ready-to-eat items on higher shelves ensures that these foods remain uncontaminated and safe to consume.
Both refrigerators and freezers rely on cold air circulation to maintain consistent temperatures and to prevent “hot spots” where bacteria can flourish. Hence, avoid overfilling or blocking the air vents with too many items. Regularly cleaning and maintaining the appliances, by removing expired or spoiled food and wiping down surfaces, will also contribute to a safe cooling environment for your food.
In summary, refrigerators and freezers are crucial tools in providing cold storage and maintaining food safety. A combination of optimal temperature settings, organized storage, and proper cleaning results in sustainable and safe food preservation.

Best Alternatives for Safe Cooling
When it comes to safely cooling foods, there are several methods that can be utilized to maintain food quality and safety. This section will cover three of the best alternatives for safe cooling: two-stage cooling, ice water baths, and blast chillers.
Two-Stage Cooling
The two-stage cooling process is a widely recommended procedure for safely cooling cooked foods. This method involves cooling the food from 135°F (57°C) to 70°F (21°C) within two hours, followed by cooling it from 70°F (21°C) to 41°F (5°C) within four hours. This relatively fast cooling process minimizes the risk of bacteria growth, ensuring that the food remains safe for consumption.
To implement the two-stage cooling process, divide large batches of cooked food into smaller, shallow containers to allow for rapid cooling. Using a cooler or refrigerator with adequate space and proper air circulation is essential to achieve the required cooling rates.
Ice Water Bath
Ice baths or chilled water baths are an excellent alternative for safely cooling foods. To use this method, place the smaller, shallow containers of cooked food into a larger container filled with ice and water, ensuring that the ice bath reaches at least halfway up the sides of the food container. Stir the food frequently to facilitate even cooling, and monitor the temperature to confirm that it reaches the desired level.
Ice water baths provide a rapid cooling rate and are especially effective for cooling dense foods or liquids, such as soups, stews, or sauces.
Blast Chillers
Blast chillers are specialized commercial equipment that rapidly cools foods by forcing cold air against the food items at high speeds. These devices can significantly reduce the cooling time compared to traditional refrigeration methods, making them suitable for large-scale food production or busy commercial kitchens.
While blast chillers can be more expensive than other methods, they offer the advantage of quickly and consistently cooling foods to safe temperatures, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and maintaining food quality.
By implementing these alternatives for safe cooling, such as the two-stage cooling process, ice water baths, or blast chillers, it is possible to ensure food safety and maintain quality, while reducing the risks associated with improper cooling techniques.
Review of Cooling Equipment
When choosing the best alternative for safely cooling foods, proper cooling equipment plays a vital role in maintaining food safety. Many appliances available on the market have impressive features designed to ensure proper cooling and temperature control.
A review of the top cooling equipment options for 2023 outlined various high-quality alternatives. Noteworthy appliances incorporate the use of stainless steel as a primary construction material, due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. Moreover, stainless steel is a reliable material for temperature regulation, ensuring efficient cooling of the foods.
One essential feature to consider when purchasing cooling equipment is a built-in thermometer for precise temperature monitoring. A precise thermometer enables users to have a clear understanding of the conditions within the appliance and allows them to make necessary adjustments to ensure safe food storage. Examples of top cooling products with built-in thermometers are high-grade refrigerators and blast chillers.
Ensuring proper food cooling is essential for preventing the growth of harmful bacteria. Therefore, some of the best cooling equipment utilizes quick-chilling methods, such as:
- Ice baths: A quick method to cool foods, especially hot liquids like soups or sauces. Immerse a container filled with the hot food into a larger container filled with ice and water.
- Blast chillers: These specialized appliances rapidly cool large quantities of food by circulating cold air at high speeds. They are ideal for commercial kitchens and catering companies.
Several other factors to consider when choosing the best alternative for safely cooling foods include the product’s energy efficiency, ease of use, and maintenance requirements. By understanding the different cooling options available and their unique features, consumers can make informed decisions to maintain high standards of food safety in their homes or commercial establishments.
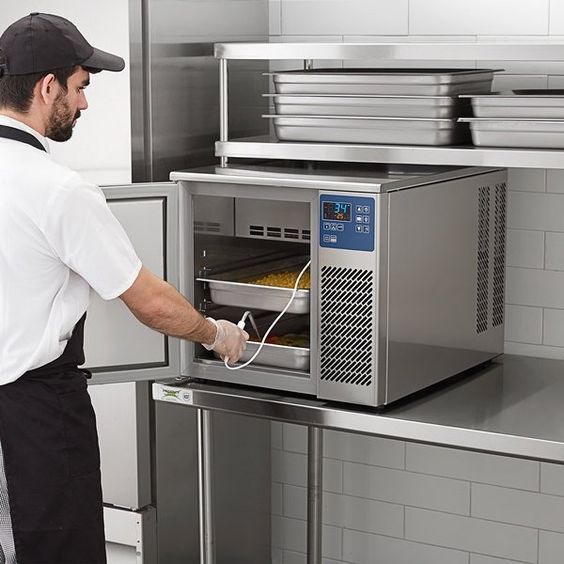

Preventing Foodborne Illness
Foodborne illnesses, also known as food poisoning, are caused by consuming contaminated foods or beverages. They can lead to serious health issues, such as vomiting, diarrhea, and even death in severe cases. Preventing foodborne illness is essential to maintaining public health and safety.
One of the key factors in preventing foodborne illness is safely cooling foods. Harmful pathogens, such as bacteria, can grow rapidly in the temperature “danger zone” between 40°F and 140°F. These pathogens can potentially cause illness in consumers. The FDA recommends cooling hot foods to 70°F within two hours and then down to 41°F or lower within an additional four hours.
When cooling foods, it’s important to use proper cooling methods, like dividing large amounts of food into smaller, shallow containers. This allows food to cool more quickly and evenly, reducing the chance of bacteria growth. Another effective method is using a food cooler, such as a refrigerator or walk-in cooler, set at the appropriate temperature to ensure rapid cooling.
Monitoring temperature is crucial in preventing foodborne illness; it’s essential to invest in an accurate thermometer that can measure the temperature within a food product to ensure it’s cooled properly. Another key aspect of food safety is following proper hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently, using clean utensils and cutting boards, and sanitizing work surfaces regularly.
In addition to safe cooling practices, here are other important guidelines to follow:
- Separate raw and ready-to-eat foods during preparation, storage, and serving
- Cook foods to their minimum internal temperatures as recommended by the FDA to kill pathogens
- Store foods at their appropriate temperatures, using a refrigerator set at or below 40°F and a freezer set at or below 0°F
By adhering to these food safety practices, one can minimize the risk of foodborne illness and contribute to a safer food supply for all.
Specific Foods and Cooling
Cooling Soups and Stews
When it comes to safely cooling soups and stews, it’s essential to use proper techniques to prevent bacterial growth. Using an ice bath is one of the most effective methods for cooling these types of dishes. Place the container containing the hot soup or stew in a larger container filled with ice and water. Stir the soup or stew frequently to evenly distribute the cooling and speed up the process. It’s crucial to ensure that the temperature drops from 135°F to 70°F within two hours, and further, reduce it to 41°F or lower within an additional four hours.
Cooling Chicken
For chicken, cooling it safely is essential to preserve its quality and taste in addition to preventing foodborne illnesses. One alternative to safely cool chicken is blast chilling, which involves rapidly reducing the temperature in a specialized chiller. This method is most suitable for large-scale commercial kitchens and may not be feasible for the average home cook.
A practical alternative for home use is to cut the cooked chicken into smaller pieces, as this will allow it to cool more rapidly. Place the chicken in a wide, shallow container and cover it, but do not seal the container completely to allow steam to escape. Refrigerate the chicken immediately and ensure that its temperature reaches 41°F or lower within a maximum of six hours.
Using appropriate cooling techniques for specific foods like soup, chicken, and stew can significantly decrease the risk of foodborne illnesses and spoilage. Additionally, storing frozen food according to recommended guidelines can contribute to maintaining the safety and quality of the products.
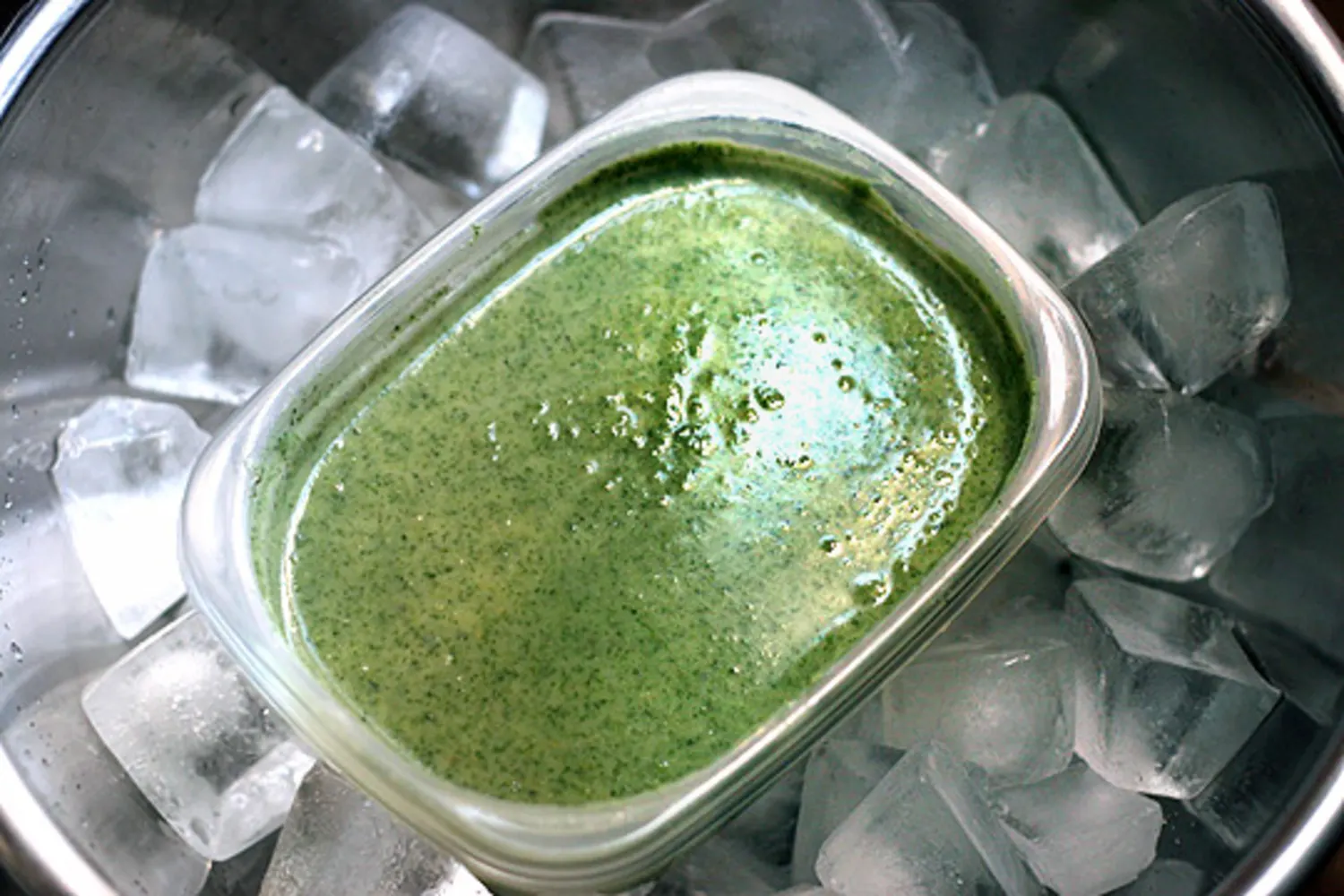

Guidelines for Safe Temperatures
Maintaining safe temperatures is crucial for food safety and proper storage. Both undercooking and overcooking food can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria. To ensure a safe and enjoyable dining experience, it’s essential to follow proper temperature control guidelines.
The first step in safe temperature control is understanding the minimum internal cooking temperatures for various types of foods. For example, beef, pork, veal, and lamb (steaks, chops, and roasts) should be cooked to a minimum internal temperature of 145°F (62.8°C) and allowed to rest for at least 3 minutes before consuming. Ground meats (beef, pork, veal, and lamb) require a higher internal temperature, reaching at least 160°F (71.1°C).
When it comes to cooling foods, it’s essential to follow specific guidelines to avoid bacterial growth. One effective method to cool food quickly and safely is using an ice water bath. This technique involves placing the container with food directly into a pan or sink filled with ice water. Stirring the food consistently while it’s cooling will help expedite the process. According to Michigan State University Extension, food should be cooled and ready to be stored within two hours from the time it was removed from heat sources.
When reheating food, ensure that all parts reach a minimum temperature of at least 165°F (73.9°C), especially when using a microwave oven. Stirring, covering, and allowing the food to stand covered for 2 minutes after reheating can help achieve even heat distribution.
Keep in mind that safe temperature control is not limited to cooking and cooling foods. Storing hot food in a refrigerator can raise the appliance’s internal temperature, potentially allowing bacteria to proliferate. To prevent this issue, allow warm food to cool to room temperature before placing it in the refrigerator. When storing food in the refrigerator, it’s essential to keep the appliance’s temperature below 40°F (4.4°C) to inhibit bacterial growth.
By adhering to these guidelines for safe temperature control, you can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and create a more enjoyable dining experience.
Effectiveness of Rapid Cooling
In the food industry, ensuring safety and maintaining quality are important aspects. One effective method to achieve this is using rapid cooling techniques. These techniques help in lowering the temperature of food items quickly, which reduces the risk of bacterial growth and spoilage. Rapid cooling is particularly crucial when handling large quantities of food and when the products are temperature-sensitive.
One method of rapid cooling is using an ice bath. This involves submerging sealed containers or resealable plastic bags filled with cooked food into a large container filled with ice and cold water. The ice bath method is simple and effectively reduces the food item’s internal temperature. Stirring the food in the ice bath can further promote faster and more even cooling.
Another efficient rapid cooling technique is vacuum cooling. This process involves placing the food into a vacuum-sealed environment where the pressure is lowered, causing the water in the food to evaporate rapidly. This evaporation process extracts heat from the food and results in rapid cooling.
Using rapid cooling methods such as ice baths and vacuum cooling not only maintains the safety and quality of the food items but also extends their shelf life. Furthermore, implementing these techniques can prevent food poisoning scenarios due to spoilage and encourage compliance with food safety regulations. In addition, the rapid cooling techniques help businesses save money by minimizing food waste caused by improper cooling.

Tips and Techniques
When it comes to safely cooling foods, there are several tips and techniques that can be utilized to ensure the process is efficient and safe. Implementing these methods will help maintain the quality of the food and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
One of the most effective methods for cooling food quickly and safely is using smaller containers or shallow pans. By dividing hot food into smaller portions, it allows for quicker cooling due to increased surface area exposure to the cold air in the refrigerator. For instance, placing a large pot of hot soup directly into the refrigerator is not recommended, since it can raise the temperature of other items in the fridge, thus putting them at risk of bacterial growth. Instead, transfer the soup into smaller containers before refrigerating.
Using shallow pans can also help with faster cooling. Placing a shallow pan filled with hot food into the refrigerator or freezer exposes more surface area to the cold air, decreasing the amount of time needed for the food to reach a safe temperature. This is especially useful for dishes like casseroles or thick sauces.
Another helpful technique is using an ice bath to cool hot food. To do this, fill a large container with ice and water, then place a smaller container with the hot food into the ice bath. Regularly stir the food to ensure even cooling throughout. Once the food has cooled down sufficiently, transfer it to the refrigerator. Remember that timely cooling is essential for food safety, as bacteria can grow rapidly between 41°F (5°C) and 135°F (57°C), known as the temperature danger zone.
In addition to these techniques, it’s also important to ensure proper storage of cooled foods. Label and date containers to keep track of how long they’ve been stored, and follow safe reheating practices when consuming leftovers. Reheating food should be done to a minimum internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to destroy any bacteria that may be present.
By following these tips and techniques, effectively and safely cooling foods becomes a simpler and more reliable process. Practicing these recommendations will help reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensure the wellbeing of everyone enjoying the food.
Conclusion
In the interest of food safety, it is crucial to find the best alternative for cooling foods effectively and efficiently. There are various methods available to achieve this goal, and each method has its unique benefits and drawbacks. The most suitable method for safely cooling foods will depend on the specific circumstances and the type of food being cooled.
One popular method for safely cooling foods is blast chilling, which involves rapidly reducing the temperature of food by exposing it to blasts of cold air. This technique ensures even and quick cooling, which reduces the risk of bacterial growth and preserves the quality and taste of the food.
Aside from blast chilling, other effective cooling alternatives include hydro coolers, glycol cooling, and thermal energy storage systems. Each of these techniques has its advantages and limitations, and some may be more appropriate for certain types of food or specific cooling requirements. For instance, hydro coolers can be ideal for cooling fruits and vegetables, while glycol cooling could be an effective solution for larger quantities of food.
In conclusion, the optimal method for safely cooling foods largely depends on the specific situation, food type, and available resources. By considering these factors and evaluating the different cooling alternatives, it is possible to select the best solution for each unique circumstance. Ultimately, this ensures the safety and quality of food while minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses and preserving the nutritional value and taste.





Leave a Reply
View Comments