The ketovore diet is a unique combination of the popular ketogenic diet and the carnivore diet, offering more flexibility and variety in food choices. With an emphasis on animal proteins, healthy fats, and a limited selection of plant-based foods, this eating plan aims to maintain nutritional ketosis to optimize the body’s fat-burning potential.
Following the ketovore diet means prioritizing animal-based foods such as meats, fish, and eggs, while reducing or excluding plant-based foods. The main objective is to achieve a state of ketosis, where the body utilizes fat stores for energy instead of carbohydrates. This occurs by limiting carbohydrate intake, which constitutes around 5% to 10% of a person’s daily energy intake on a strict ketogenic diet.
Understanding the difference between ketovore and traditional keto diets is crucial for individuals considering this way of eating. By allowing for more flexibility, the ketovore diet can better fit into one’s lifestyle and preferences, making adherence to the plan more manageable. It’s essential to learn about the foods to eat and avoid, along with potential benefits and drawbacks before beginning this unique diet journey.
Reader's Roadmap
Understanding the Ketovore Diet
The Ketovore Diet is a unique approach to nutrition that combines elements of the popular ketogenic diet and the carnivore diet. By focusing on a low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein intake, this hybrid diet aims to provide the benefits of both diets while minimizing potential drawbacks.
In the Ketovore Diet, the primary goal is to achieve a state of ketosis. This metabolic state occurs when the body starts burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. The shift in fuel source is believed to contribute to weight loss and various health improvements.
As a variation of the keto diet, Ketovore places a strong emphasis on animal-based foods while reducing or excluding plant-based sources. Traditional keto macros typically consist of around 75% fat, 25% protein, and 5% carbs. The Ketovore Diet, however, allows for some flexibility, leaning towards a higher protein ratio and potentially more carbohydrates.
One of the main distinctions between the Ketovore and the carnivore diet is the level of strictness. While the carnivore diet solely focuses on consuming meat and animal products, the Ketovore Diet incorporates some features of the keto diet, such as the possible inclusion of low-carb plants. This makes it a more flexible option for individuals seeking the benefits of a strict carnivore diet without eliminating other food groups entirely.
To maintain consistent results with the Ketovore Diet, it is crucial to monitor macronutrient ratios while experimenting with various fat and protein sources. This allows individuals to find the right balance that works best for their metabolic needs and health goals.
In conclusion, the Ketovore Diet offers an alternative approach to low-carb, high-fat eating patterns. Combining aspects of both the ketogenic and carnivore diets provides a flexible and effective way to achieve ketosis and improve overall health.
The Basics of Ketovore Diet
The Ketovore Diet is a combination of both the ketogenic diet and carnivore diet, focusing primarily on animal products with minimal plant-based foods. This diet aims to utilize fat as the primary fuel source while increasing protein intake and keeping carbohydrate consumption extremely low.
Foods to Include
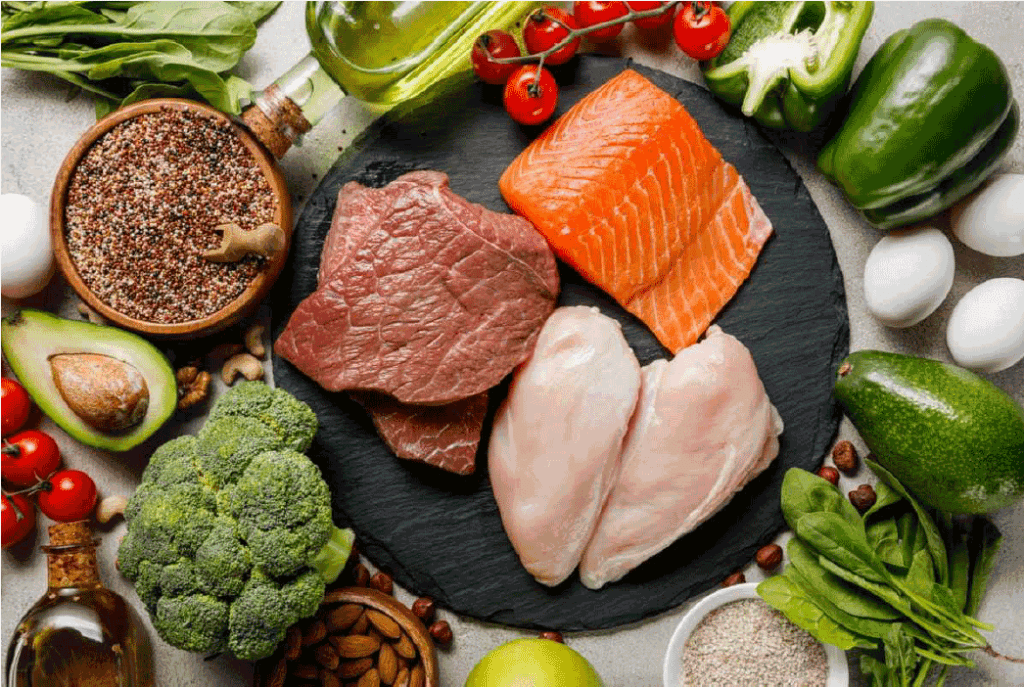

The Ketovore diet emphasizes the consumption of meats, seafood, eggs, dairy, and healthy fats from various sources. Here’s a list of some common food choices for individuals following this diet:
- Meat and Poultry: Beef, pork, lamb, game, chicken, turkey, and other types of poultry are all encouraged on the Ketovore Diet.
- Fish and Seafood: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are rich in healthy fats and protein. Shellfish, such as crab and shrimp, are also acceptable.
- Eggs: Eggs are a versatile and nutrient-dense food that can be incorporated into a Ketovore diet.
- Dairy and Cheese: Full-fat dairy products like cheese, butter, and cream can be included in moderation for additional fat content.
- Healthy Fats: Coconut oil, avocado oil, and animal fats like lard or tallow provide necessary energy and nutrients.
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, plus non-starchy vegetables like zucchini, cauliflower, and broccoli can be included sparingly.
- Nuts and Seeds: Macadamia nuts, pecans, and brazil nuts are compatible with the Ketovore Diet due to their high fat and low carb content. Seeds, such as chia or flax, should be consumed in moderation.
- Low-Sugar Fruits: Berries, including blackberries, raspberries, blueberries, and strawberries can be consumed in small quantities.
Foods to Avoid
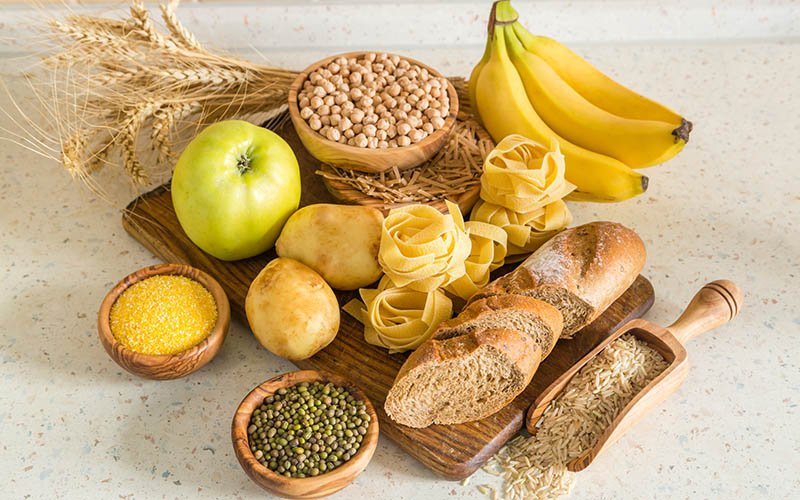

As the Ketovore Diet is primarily based on animal products, it’s crucial to avoid high-carb foods that might disrupt the state of ketosis. Some foods to stay away from include:
- Grains: Wheat, oats, rice, quinoa, corn, and any foods made from them like bread, pasta, and breakfast cereals should be avoided.
- Starchy Vegetables: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, peas, and root vegetables like carrots and beets are typically high in carbohydrates and not ideal for this diet.
- High-Sugar Fruits: Bananas, grapes, apples, cherries, and other high-sugar fruits should be limited or avoided.
- Processed Foods: Cakes, cookies, pastries, and other heavily processed products containing refined sugars and unhealthy fats are not recommended.
- Sugary Beverages: Sodas, sweetened teas, and other sugar-laden drinks should be replaced with water or unsweetened alternatives.
In summary, the Ketovore Diet focuses on the consumption of animal products while limiting or avoiding plant-based foods and sugary items. By doing so, it aims to achieve the benefits of both the ketogenic and carnivore diets and serve as a middle ground for those looking to transition between the two.
Health Benefits of the Ketovore Diet
Weight Loss and Metabolic Health
The Ketovore Diet is a high-protein, low-carb eating plan that has been shown to be effective for weight loss and improved metabolic health. By consuming higher amounts of protein and fat, this diet can help increase satiety after meals, reducing overall calorie intake. In addition, it helps to regulate insulin and blood sugar levels, which may be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Some people on the Ketovore Diet also incorporate intermittent fasting, further supporting weight loss and blood sugar control. Overall, this low-carbohydrate approach puts the body into a metabolic state where it uses ketones for energy instead of glucose, which can lead to significant weight loss for some individuals.
Other Health Benefits
Apart from weight loss and metabolic health, the Ketovore Diet has been associated with other positive aspects as well. Improved mental clarity is often reported by those following this diet, which may be attributed to the increased production of ketones and stable blood sugar levels. More stable blood sugar levels contribute to more consistent energy levels throughout the day, reducing the likelihood of energy crashes or mood swings.
The Ketovore Diet also emphasizes the consumption of healthy fats, which are known to support heart health by reducing inflammation and maintaining a healthy cholesterol balance. These healthy fats can help to reduce the risk of heart disease, as they may lower levels of LDL cholesterol and increase levels of HDL cholesterol.
Potential Risks and Concerns
While the Ketovore Diet offers numerous health benefits, there are potential risks and concerns that should be considered. One concern is the relatively low intake of carbohydrates, which can lead to a decreased intake of essential nutrients found in plant-based foods. This may result in nutrient deficiencies if not planned properly. Additionally, some individuals may not respond well to a high-fat diet and may experience gastrointestinal issues or negative effects on heart health.
It’s important for anyone considering the Ketovore Diet to consult with a healthcare professional before making major dietary changes, in order to ensure that they are meeting their nutritional needs and addressing any potential health concerns.
Meal Planning for the Ketovore Diet
Coffee, Tea, and Beverages
When following the Ketovore Diet, it is essential to maintain proper hydration. Drinking water should be your primary beverage of choice. However, you can also include unsweetened coffee and tea as options in your meal plan. Those on a ketovore diet often prefer to add full-fat cream or butter to their coffee for added calories and flavor. It is important to avoid sugar, sweeteners, and high-carb beverages such as fruit juices and sodas, as they can interfere with maintaining a state of ketosis.

Tips on Seasoning and Spices
Seasoning and spices can make a significant difference when it comes to making your Ketovore Diet meals more enjoyable. A simple strategy involves using salt and pepper to enhance the natural flavors of your animal-based foods. However, you can also experiment with various herbs and spices to add variety. Stick to seasonings that are low in carbohydrates and avoid using premixed spice blends that may contain hidden sugars or additives. Some popular options for the Ketovore Diet include:
- Garlic powder
- Onion powder
- Paprika
- Cayenne pepper
- Oregano
- Thyme
Remember to always check the labels of the spices you use, and prioritize those with minimal additives and carbs.
Ketovore Meal Plan Example
Here is a brief example of a Ketovore meal plan to help you get started:
Day 1:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with cheddar cheese, bacon, and coffee with heavy cream
- Lunch: Grilled chicken thighs with a side of homemade cream cheese dip
- Dinner: Pan-seared ribeye steak with butter and a side of garlic sautéed spinach
- Snacks: Pork rinds or a hard-boiled egg
Day 2:
- Breakfast: Omelette with mushrooms, spinach, and mozzarella, served with black coffee
- Lunch: Roast beef roll-ups with sliced avocado and a side of green tea
- Dinner: Baked salmon with a lemon-butter sauce and a side of roasted asparagus
- Snacks: Cheese crisps or beef jerky
Creating a meal plan can be highly beneficial in ensuring you stay consistent with your Ketovore Diet, which can help you achieve long-term success. Remember to keep drinks and snacks low-carb, and don’t be afraid to experiment with various seasonings and spices to enhance the flavor of your meals.
Comparing Ketovore with Other Diets
Ketovore versus Keto Diet
The Ketovore Diet focuses on consuming high amounts of animal-based fat and protein while limiting carbohydrate intake, similar to the Keto diet. However, there are key differences between the two. The traditional Keto diet emphasizes consuming 75% of calories from fat, 25% from protein, and 5% from carbohydrates. On the other hand, the Ketovore Diet allows for more flexibility in macro ratios, generally leaning towards a higher protein intake and potentially even allowing for more carbohydrates.
Both diets can be effective for managing blood sugar levels and may be suitable for people with diabetes due to their low-carb nature. However, the increased protein consumption in the Ketovore Diet might be more appealing to certain individuals, particularly those with higher protein requirements or those who prefer animal-based foods.
Ketovore versus Carnivore Diet
While both Ketovore and Carnivore diets prioritize animal-based foods, they differ in their approach to other food groups. The Carnivore Diet focuses exclusively or almost exclusively on animal protein, emphasizing fish, seafood, meat, eggs, bone marrow, dairy, salt, and water, with little to no plant-based foods. Some Carnivore dieters may include a small portion of herbs, leafy greens, or berries.
In contrast, the Ketovore Diet is more flexible regarding the inclusion of plant-based foods, although they are still limited. This flexibility might be more suitable for people who want to incorporate small amounts of vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, legumes, or other plant-based options into their diet.
Ketovore Versus Plant-Based Diets
Ketovore and plant-based diets differ significantly in their food source emphasis. The Ketovore Diet prioritizes animal-based foods, while plant-based diets focus on consuming vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, seeds, and nuts. Plant-based diets can take various forms, from vegan (completely removing animal products) to vegetarian (excluding meat but may include dairy or eggs) or even pescatarian (including fish but not other meats).
Plant-based diets are known for their high fiber content and potential health benefits, such as reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. Those following a Ketovore Diet might want to consider incorporating some plant-based foods like avocados, which are high in healthy fats, and low-carb vegetables like leafy greens to ensure they benefit from essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
While the Ketovore Diet may work for some, others might prefer a more balanced approach by combining aspects of various diets or selecting one that aligns best with their individual nutritional needs, lifestyle, and preferences.






Leave a Reply
View Comments