Semaglutide, a medication prescribed for treating type 2 diabetes has shown considerable success in managing blood glucose levels and supporting weight loss. However, patients may experience some side effects while taking this drug, with tiredness being a commonly reported issue. The fatigue that patients might experience while using semaglutide can manifest in various ways, such as trouble concentrating or feeling overwhelmed.
Although the exact cause of this tiredness is not entirely understood, it is important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of this potential side effect. Researchers are continually studying the effects of semaglutide and other similar medications to better understand the mechanisms behind these side effects, which could lead to improved treatments and management strategies for patients using these drugs.
In this article, we will explore the connection between semaglutide and tiredness, discussing its potential causes and how patients may cope with this side effect while taking the medication. Understanding the risks and benefits of semaglutide can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment and improve their overall health.
Reader's Roadmap
Understanding Semaglutide
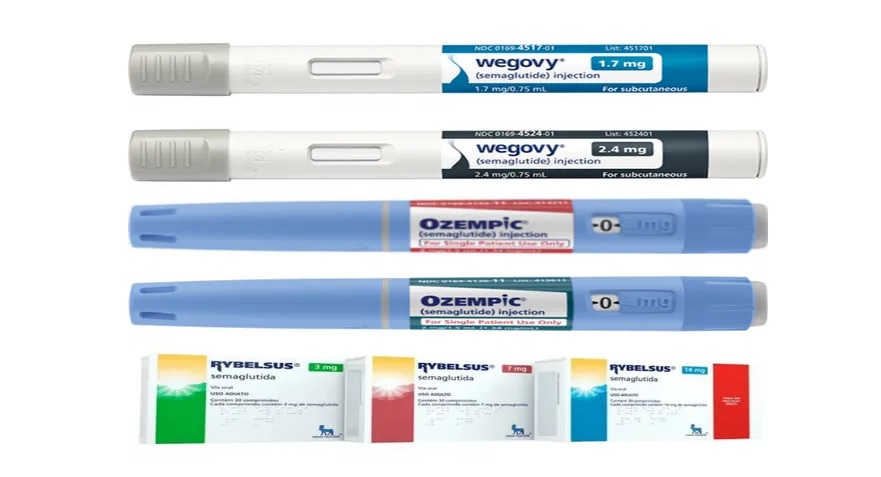
Semaglutide is a medication commonly prescribed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and to support weight loss. It belongs to a class of drugs called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, which help regulate blood sugar levels. Semaglutide is available in three forms: Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus. These medications share similar characteristics but have different purposes and administration methods.
Ozempic is an injectable form of semaglutide and is primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes. It aids in lowering blood sugar levels and has been found to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in adults with diabetes.
Wegovy, also injectable, is primarily prescribed for weight management. It has been proven helpful for individuals who have not responded to other weight loss methods or have difficulty maintaining weight loss. Wegovy is typically used along with a reduced-calorie meal plan and increased physical activity to achieve the desired results.
Rybelsus is an oral tablet form of semaglutide and is another option for the management of type 2 diabetes. It works similarly to Ozempic, by lowering blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events in adults with diabetes.
It’s important to note that fatigue is a common side effect experienced by individuals taking semaglutide-based medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus. Most users report feeling tired initially when starting the therapy, but this effect typically subsides after a few weeks as the body adjusts to the medication. There may be other manageable strategies, such as proper exercise and diet, to help alleviate fatigue during the adjustment period.
While nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are the most common side effects associated with semaglutide, it is essential for users to be aware of the potential for more severe, albeit rare, side effects. These may include pancreatitis and allergic reactions, which require immediate medical attention.
Semaglutide and Type 2 Diabetes
Semaglutide is a type of medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels and insulin resistance. It is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a class of drugs that helps regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of insulin and inhibiting the release of glucagon in the liver.
Administered as a subcutaneous injection, semaglutide helps people living with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels, keeping them stable throughout the day. By mimicking the action of GLP-1, a naturally occurring hormone that regulates glucose metabolism, semaglutide promotes healthier insulin production and reduces the amount of sugar released by the liver.
Semaglutide is used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. The SUSTAIN (Semaglutide Unabated Sustainability in Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes) clinical program demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c levels and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) at 1mg/weekly and 2mg/weekly doses. This is important for lowering the risk of complications, such as heart attack, stroke, or death in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart or blood vessel disease.
Compared to other GLP-1 receptor agonists, semaglutide has some distinct advantages. Unlike some of its counterparts, it can be taken as an oral medication instead of an injection, offering more convenience for people managing their diabetes. However, like many medications, semaglutide comes with potential side effects.
Some common side effects of semaglutide include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. While these gastrointestinal symptoms might be mild or short-lived, they can potentially contribute to feelings of fatigue for some users. Additionally, semaglutide can lead to a reduction in caloric intake, which can also make a person feel tired. It is crucial for individuals taking semaglutide to monitor their side effects and communicates with their healthcare provider to find the right balance of medication, diet, and exercise in managing their type 2 diabetes.
Usage and Dosage of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is an effective treatment for both type 2 diabetes and weight management. It comes in different brand names such as Ozempic, Rybelsus, and Wegovy, and is available in injectable and oral formulations. In order to ensure safety and efficacy, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and administration guidelines.
The dosage of semaglutide varies depending on the individual’s condition and the specific medication being used. For type 2 diabetes management, the injectable form of semaglutide (Ozempic) is typically started with an initial dose of 0.25 mg once a week. After four weeks, the dose may be increased to 0.5 mg once weekly, based on the patient’s response and tolerance. If additional glycemic control is needed, the dose can be further increased to a maximum of 1 mg per week.
In contrast, the oral form of semaglutide (Rybelsus) is started at a dose of 3 mg daily for the first 30 days. After this initial period, the dosage is increased to 7 mg daily. If further glycemic control is warranted, the dose can be increased up to a maximum of 14 mg per day.
For weight management, the injectable form of semaglutide (Wegovy) is administered with a different dosing schedule. The starting dose is 0.25 mg once weekly for the first four weeks, followed by 0.5 mg once weekly for the next four weeks. The dose is then gradually increased by 0.5 mg every four weeks, up to a maximum of 2.4 mg per week.
It is essential to note that some individuals taking semaglutide, especially at higher doses, may experience tiredness and fatigue. These side effects, however, may lessen as the body adjusts to the medication. If they persist or become severe, patients should consult their healthcare provider.
In summary, semaglutide is available for both injectable and oral administration, with different dosing guidelines for type 2 diabetes management and weight management. Following the prescribed dosage and schedule is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes. It is important to remember that side effects like tiredness may occur, but they may subside as the body adjusts to the medication.
Potential Side Effects of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and help control blood sugar levels. It’s usually administered in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise regimen. Despite its benefits, it’s essential to be aware of its potential side effects. The most commonly reported side effects of semaglutide are gastrointestinal in nature, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
It’s important to note that these gastrointestinal side effects typically subside after a few weeks of using the medication. However, additional side effects may include constipation, hypoglycemia, dizziness, gas, bloating, and indigestion. Some patients may also experience headache or a change in appetite while taking semaglutide.
In the context of fatigue, semaglutide has the potential to cause tiredness as an indirect result of its gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The level of tiredness a person experiences while taking semaglutide may also be influenced by the method of administration (pill or injection) and dosage.
Rare but serious side effects have been reported in some patients, such as allergic reactions and seizures. If someone experiences any signs of an allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or hives, they should seek immediate medical attention. Similarly, if seizures occur while taking semaglutide, a healthcare professional must be informed as soon as possible.
In conclusion, semaglutide has several potential side effects that range from gastrointestinal issues to fatigue and more serious concerns like allergic reactions or seizures. Patients should closely monitor their reactions to the medication and report any unexpected or severe symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Weight Loss and Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a medication initially developed for the treatment of diabetes that has gained attention for its potential benefits in weight loss and weight management. The drug works by mimicking the natural hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which helps regulate blood sugar levels and suppress appetite.
Studies have shown promising results in using semaglutide for weight loss. In a research study, after 68 weeks of treatment, half of the participants using semaglutide lost 15% of their body weight, while nearly a third lost 20%. In comparison, participants who only incorporated lifestyle changes lost around 2.4% of their weight. These findings suggest that semaglutide has a significant impact on body weight and obesity management.
However, semaglutide may cause side effects that can affect a person’s energy levels. Among these side effects are nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which can lead to a reduction in caloric intake. This decrease in calorie consumption may result in increased feelings of tiredness. Additionally, fatigue and tiredness have been reported as side effects of semaglutide, although these symptoms are not considered common.
The dosage and method of administration of semaglutide, either as a pill or an injection, can also influence how tired an individual feels while taking the medication. Proper dosing and monitoring by a healthcare provider can help address possible fatigue and tiredness concerns.
In conclusion, semaglutide can be a potentially effective option for weight loss, particularly in addressing obesity and helping individuals manage their body weight. However, it is important to consider its side effects, including possible fatigue or tiredness, when evaluating its suitability for individual weight management plans.
Serious Health Risks Associated with Semaglutide
Semaglutide is commonly prescribed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, as its primary function is to help regulate blood sugar levels. Despite its effectiveness in this regard, it is important to be aware of the potential health risks associated with its usage. Some of the most serious health risks that patients taking semaglutide could encounter include pancreatitis, thyroid cancer, stroke, and gallbladder disease.
Pancreatitis is a particularly concerning side effect, as it can result in severe abdominal pain and even lead to more serious complications if left untreated. Physicians may advise patients taking semaglutide to closely monitor their symptoms and report any signs of acute pancreatitis, such as persistent pain in the upper abdominal region, nausea, and vomiting. Mayo Clinic has reported occurrences of pancreatitis in patients using semaglutide.
Thyroid cancer and thyroid C-cell tumors have also been observed in rodents during clinical trials of semaglutide. Although this has not been definitively proven in humans, there is still cause for concern, and those taking this medication should be closely monitored for symptoms of thyroid cancer or tumors. Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) is another potential thyroid-related condition linked to the use of semaglutide.
Stroke poses another potential health risk, although the connection between semaglutide and stroke is not yet fully understood. Patients with existing risk factors for stroke, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes, should discuss the potential risks and benefits of using semaglutide with their healthcare provider.
Gallbladder disease, cholelithiasis, and gallstones are additional concerns for those using semaglutide. If a patient experiences gallbladder problems while taking this medication, they should seek medical advice immediately. In some cases, discontinuation of the medication may be necessary.
Finally, kidney problems like acute kidney injury and impaired kidney function are potential health risks associated with semaglutide. Patients with pre-existing kidney disease or risk factors for kidney issues should exercise caution when using this medication and have regular check-ups to monitor kidney function.
Patients taking sulfonylureas are advised to consult with their healthcare provider, as these medications may interact with semaglutide and potentially increase the risk of adverse side effects. Additionally, anyone experiencing symptoms of allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis and angioedema, should seek medical help immediately.
In conclusion, it is essential for patients prescribed semaglutide to be aware of its potential health risks and communicate closely with their healthcare provider. Regular monitoring of symptoms and a proactive approach to reporting concerning side effects are vital to minimizing the risk of developing serious health complications while taking this medication.

Interactions and Precautions with Semaglutide
Semaglutide, a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, may cause tiredness as one of its side effects. While taking this medication, it is essential to consider possible drug interactions and precautions to ensure its safe use and avoid complications.
Semaglutide has 248 known drug interactions, including major, moderate, and minor interactions. Some of the common medications that interact with semaglutide are glimepiride and metformin. Combining these medications may require dose adjustments or close monitoring by a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of side effects or diminished effectiveness of the drugs.
In addition to drug interactions, semaglutide also has some alcohol and food interactions. Although the specific effects of alcohol on semaglutide have not been studied extensively, it is generally advised to minimize alcohol consumption while taking diabetes medications. Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels, which may disrupt the effectiveness of semaglutide or lead to unwanted side effects.
Taking semaglutide in tablet form, such as Rybelsus, may require additional precautions. The absorption of semaglutide can be affected by certain foods, so it is important to follow the specific instructions provided by a healthcare professional. Typically, Rybelsus should be taken with a small amount of plain water at least 30 minutes before the first meal of the day.
Vitamins and minerals may also have a potential impact on the effectiveness of diabetes medications, including semaglutide. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before adding new vitamin or mineral supplements to one’s routine to ensure a safe combination. Keep in mind that a balanced diet and regular physical activity remain crucial components of managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in the effectiveness of medications like semaglutide.
In conclusion, when taking semaglutide, it is essential to consider the potential drug interactions, alcohol and food interactions, and the role of vitamins and minerals in maintaining its effectiveness. As always, consulting a healthcare professional is the best way to ensure safe and effective use of medication.
Semaglutide and Other Medications
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, commonly used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is a protein that functions by mimicking a gut hormone, leading to the release of insulin from the pancreas, blocking the liver from releasing sugar, and slowing down the rate at which food leaves the stomach. However, some patients using semaglutide may experience side effects such as tiredness. This effect could be attributed to a reduction in caloric intake, as well as the medication’s other side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
It is essential to consider the interaction of semaglutide with other medications when evaluating tiredness as a potential side effect. For instance, sulfonylureas, prescribed for type 2 diabetes management, can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), a condition that may lead to fatigue1. People with any form of diabetes should be cautious about the combined use of semaglutide and other medications that may affect blood sugar levels.
Liraglutide is another GLP-1 receptor agonist similar to semaglutide, and both medications share common side effects, including tiredness and fatigue. Patients on either of these medications may potentially experience weariness as they require time to adjust to the medication and its effects on the body.
Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes, and those using semaglutide or other GLP-1 receptor agonists should be monitored for the development or worsening of this condition. While there is no direct link between semaglutide and retinopathy, poorly managed blood sugar levels can contribute to the condition’s progression, which may indirectly result in tiredness or fatigue.
Moreover, it is crucial to note that semaglutide is not recommended for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis1. Therefore, it is essential for patients and healthcare providers to carefully evaluate the suitability of semaglutide and other diabetes medications based on individual health conditions and needs. In conclusion, monitoring and adjusting medication doses, as well as considering potential interactions with other drugs, may help alleviate tiredness and other side effects associated with semaglutide.
Administration of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a medication commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes and assist in effective weight management. It is known for its ability to help regulate blood sugar levels and lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, or death in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart or blood vessel disease. The administration of semaglutide involves subcutaneous injections, meaning the medicine is injected just beneath the skin.
To ensure the optimal absorption and effectiveness of semaglutide, it is advised to administer the injection during or within an hour before the intake of a meal. This timing helps reduce the possibility of side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea and provides better control over blood sugar levels.
The most common injection sites for semaglutide are the abdomen, upper arm, and thigh. It is essential to rotate the injection sites to avoid any skin irritation or discomfort. Always clean the injection site with an alcohol swab before administering the medication to reduce the risk of infection.
Prior to administering semaglutide, make sure all required materials are readily available, such as a new, sterile syringe, a clean alcohol swab, and the medication vial. Begin by washing your hands thoroughly to maintain hygiene. Prepare the syringe according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring that the correct dosage is drawn.
Once the injection site is cleaned and the syringe is prepared, pinch the skin around the site to create a small fold. Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle into the fold, and slowly inject the medication. Carefully remove the needle and discard the used syringe in a designated sharps container.
In conclusion, the proper administration of semaglutide is crucial for effective treatment and control of type 2 diabetes or weight management. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting semaglutide treatment, and notify them if any concerning side effects or complications arise during its use.

Uncommon Side Effects of Semaglutide
Semaglutide, a medication used for managing type 2 diabetes and weight loss, can occasionally cause uncommon side effects that may affect some individuals. One of these side effects is hair loss, which is experienced by a small percentage of people taking the drug. Although hair loss can be an unpleasant experience, it is not considered a life-threatening side effect.
Another less common side effect is a sensation of fullness after taking the medication. This feeling of fullness can sometimes lead to reduced appetite, which may contribute to weight loss in some individuals. However, it is essential to monitor your food intake and maintain a balanced diet while experiencing this side effect.
Semaglutide has also been reported to affect heart rate in some cases. People taking the drug might experience either increased or decreased heart rate, which could be a concern for those with existing heart conditions. If you notice any changes in your heart rate while taking semaglutide, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare professional.
Hypersensitivity reactions, although rare, can occur in some individuals taking semaglutide. These reactions can manifest as skin rashes, itching, or swelling. If you suspect that you may be experiencing a hypersensitivity reaction to semaglutide, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Lastly, semaglutide carries a warning regarding the risk of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). This is a rare form of cancer that can develop in the thyroid gland’s C-cells. While the risk is low, it is essential to be aware of this potential side effect and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
In conclusion, while semaglutide has numerous benefits for managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss, it is essential to be aware of its potential uncommon side effects. If you experience any of these side effects or have concerns about taking semaglutide, consult your healthcare professional for guidance and appropriate management.





Leave a Reply
View Comments